DynamoDB
Fully managed NoSQL database that provides low-latency access at scale
Usage patterns
- Apps needing low-latency NoSQL database able to scale storage and throughput up or down without code changes or downtime
- Mobile apps and gaming
- Sensor networks
- Digital and serving
- E-commerce shopping carts
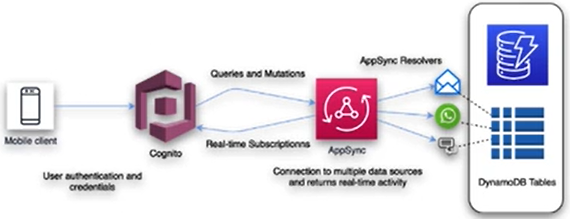
Cost
- Three components:
- Provisioned throughput capacity (per hour)
- Indexed data storage (per GB per month)
- Data transfer in or out (per GB per month)
Performance
- SSDs and limiting indexing on attributes provides high throughput and low latency
Define provisioned throughput capacity required for your tables
- Fault tolerance: automatically synchronously replicates data across 3 data centers in a region
Durability and avaiability
- Protection against individual machine or facility failures
- DynamoDB Streams allows replication across regions
- DynamoDB Streams enables tables data activity replicated across geographic regions
Scalability and elasticity
- No limit to data storage, automatic storage allocation, automatic ddata partition
Interfaces
- REST API allows management and data interface
- DynamoDB select operation creates SQL-like queries
Anti-patterns
- Port application from relational database
- Joins or complex transactions
- Large data with low I/O rate
- Blob (Binary Large Object) data > 400KB, S3 better choice
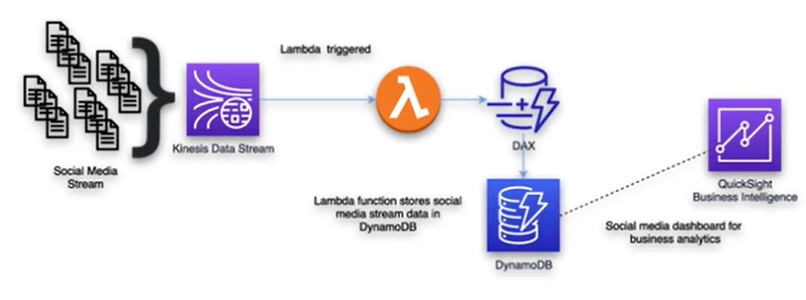
Operational Characteristics of DynamoDB in detail
- DynamoDB tables
- Attributes are the columns
- Items are the rows
- Tables are a collection of items
- Must have a primary key, two types:
- Partition key: primary key with one attribute called the hash attribute
- DynamoDB has function determines the partition where an item is located
- Composite primary key: partition key plus sort key (range attribute) where all items with the same sort key are located together ordered by sort key value
- Partition key: primary key with one attribute called the hash attribute
- No limit to number of items (rows) in a table
- Maximum item size is 400KB
- DynamoDB has two models of consistency: eventual and strong consistency
- Eventually consistent reads are the default
- Achieves maximum read throughput (Performance +)
- May return stale data (Accuracy -)
- Strongly consistent reads
- Returns result representing all prior write operations
- Always accurate data returned (no stale data) (Accuracy +)
- Increased latency with this option (Performance -)
- Eventually consistent reads are the default
- Atomicity, consistency, islolation, and durability (ACID)
- Support for ACID transactions using transactional read and write APIs
- ACI across one or more tables in one account and region
- Use for transactions that require coordinated inserts, updates, or deletes to multiple items as part of one logical operation
- Cost versus performance - two capacity modes
- On-demand capacity
- DynamoDB automatically provisions capacity based on your workload, up or down
- Provisioned capacity
- Specify read capacity units (RCUs) and write capacity units (WCUs) per second for your application
- One RCU equals one strongly consistent read or two eventually consistent reads per second for items to up to 4 KB
- One WC equals one write per second for items to up to 1 KB
- Can use auto scaling to automatically calibrate our table’s capacity
- Helps manage cost
- On-demand capacity
- DynamoDB Global tables
- Specifiy multple in which our table is available
- DynamoDB propagates all changes across all regions
- Any change to an item in any replica is propagated to all other replicas
- New items propagated within seconds
- Uses last-writer-wins reconciliation with concurrent updates
- When a table in a region has issues, application directs to a different region
Sources
- https://www.trek10.com/blog/best-practices-for-secondary-indexes-with-dynamodb
- https://www.trek10.com/blog/easier-dynamodb-unit-testing-with-python
- https://codeburst.io/inverted-index-gsi-overloading-and-sparse-index-in-dynamodb-cbfb520b2696
- https://codeburst.io/dynamodb-data-modeling-7f11950b25bf
- https://blog.thepolyglotprogrammer.com/10-things-you-should-know-about-dynamodb-e5b9593e6340