AWS EMR
Uses Hadoop to distribute data and processing across a resizeable cluster of EC2 instances
Usage patterns
- Reduces large processing problems and data sets into smaller jobs and distributes them across many compute nodes in a Hadoop cluster
- Log processing and analytics
- Large ETL data movement
- Ad targeting, click stream analytics
- Predictive analytics
Cost
- Pay for the hours the cluster is up
- EC2 pricing options (On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot)
- EMR price is in addition to EC2 price
Performance
- Driven by type/number of EC2 instances
- Ephemeral or long-running
- Fault tolerant for core node failures and continues job execution if a slave node goes down
Durability and availability
- Starts p a new node if core node fails
- Will not replace nodes if all nodes in the cluster fail
- Monitor for node failures through CloudWatch
Scalability and elasticity
- Resize your running cluster: add core nodes, add/remove task nodes
Interfaces
- Tools on top of Hadoop: Hive, Pig, Spark, HBase, Presto
- Kinesis Connector: directly read and query data from Kinesis Data Streams
Anti-patterns
- Small data sets; Made for big data sets
- OLTP/ACID transactions; RDS is a better choice
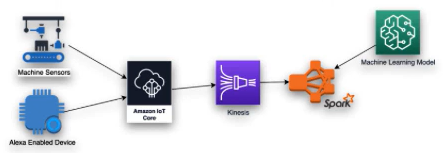
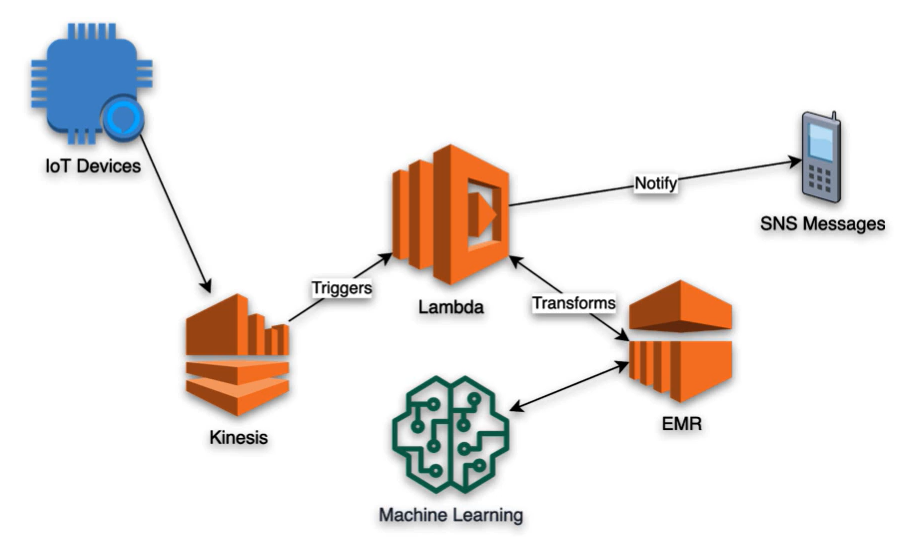
Analytics Solutions Patterns with EMR
Uses the map-reduce technique to reduce large processing problems into small jobs distributed across many nodes in a Hadoop cluster
- On-Demand big data analyitcs
- Event-driven ETL
- Machine Learning predictive analytics
- Clickstream analysis
- Load data warehousees
EMR Cluster ETL Processing
- More flexible and powerful than Spark
- Can use Spark on EMR, but also have other options:
- Flink: Framework and distributed processing engine for stateful computations over unbounded and bounded data streams
- Hadoop: Framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers
- Spark: Distributed general-purpose cluster-computing framework
- Sqoop: Command-line interface application for transferring data between relational databases and Hadoop
- TensorFlow: Machine Learning library
- Zepplin: Web-based notebook for data-driven analytics
- Hive: A SQL-like interface to query data stored in various databases and file systems that integrates with Hadoop. Alternative to Glue Data Catalog
- Hue: Web interface for analyzing data with Hadoop
- Presto: High performance distributed SQL query engine for big data
EMR Components
EMR is built upon clusters (or collections) of EC2 instances
- The EC2 instances are called nodes, all of which have roles (or node type) in the cluster
- EMR installs different software components on each node type, defining the node’s role in the distributed architecture of EMR
- Three types of nodes in an EMR cluster
- Master node: manages the cluster, running software components to coordinate the distribution of data and tasks across other nodes for processing
- Core node: has software components that run tasks and store data in the HDFS on your cluster
- Task node: node with software components that ONLY runs tasks and does NOT store data in HDFS
EMR Cluster - Work
Options for submitting work to your EMR cluster
- Script the work to be done as functions that you specify in the steps you define when you create a cluster
- This approach is used for clusters that process data and then terminate
- Build a long-running cluster and submit steps (containing one or more jobs( to it via the console, the EMR API, or the AWS CLI
- This approach is used for clusters that process data continuously or need to remain available
- Create a cluster and connect to the master node and/or other nodes as required using SSH
- This approch is used to perform tasks and submit queries, either scripted or interactively, via the interfaces of the installed applications
EMR Cluster - Processing Data
At launch time, you choose the framework and applications to install to achieve your data prcoessing needs. You submit jobs or queries to installed applications or run steps to process data in your EMR cluster
- Submitting jobs/steps to installed applications
- Each step is a unit of work that has instructions to process data by software installed on the cluster
- Example: Submit a request to run a set of steps
EMR Cluster - Lifecycle
- Provisions EC2 instances of the cluster
- Runs bootstrap actions
- Installs applications such as Hive, Hadoop, Sqoop, Spark
- Connect to the cluster instances; cluster sequentially runs any steps that specified at creation; submit additional steps
- After steps complete the cluster waits or shuts down, depending on config
- When all instances are terminated, the cluster moves to COMPLETED state
EMR Architecture - Storage
Architected in layers. Storage: file systems used by the cluster
- HDFS: distributes the data it stores across instances in the cluster (ephemeral)
- EMR File System (EMRFS): directly access data stored in S3 as if it were a file system like HDFS
- Local file system: EC2 locally connected disk
EMR Architecture - Cluster Management
YARN (Yet Another Resource Manager)
- Centrally manage cluster resources
- Agent on each node that keeps the cluster healthy, and communicates with EMR
- EMR defaults to scheduling YARN jobs so that jobs will not fail when task nodes running on spot instances are terminated
EMR Architecture - Data Processing Frameworks
Framework layer that is used to process and anaylze data Different frameworks are available:
- Hadoop MapReduce:
- Parallel distributed applications that use Map and Reduce functions (e.g. Hive)
- Map function maps data to sets of key-value pairs
- Reduce function combines the key-value pairs and processes the data
- Spark
- Cluster framework and programming model for processing big data workloads
- Parallel distributed applications that use Map and Reduce functions (e.g. Hive)
EMR Architecture - Application Programs
- Supports many application programs
- Create processing workloads
- Use machine learning algorithms
- Create stream processing apps
- Build data warehouses and data lakes
EMR Applications and Categories
EMR supports many hadoop applications
- Spark
- Hive
- Presto
- HBase
Data scientists and engineers use EMR to run analytics workflows using these tools along with Hue and EMR Notebooks
Several important categories of EMR applications
- Data Processing
- SQL
- NoSQL
- Interactive Analytics
Data Processing Applications
Apache Spark
- Hadoop ecosystem engine used process large data sets very quickly
- Runs fault-tolerant resilient distributed datasets (RDDs) in-memory, and defines data transformations
- Includes Spark SQL, Spark Streaming, MLlib, and GraphX
Apache Flink
- Streaming dataflow engine that allows you to run real-time stream processing on high-throughput data sources
- Supports APIs optimized for writing both streaming and batch applications
SQL Applications
Apache Hive
- Data warehouse and analytics package that runs on top of Hadoop
- Allows you to structure, summarize, and query data
- Supports map/reduce functions and complex extensible user-defined data types like JSON and Thrift
- Can process complex and unstructured data sources such as text documents and log files
Presto
- SQL query engine optimized for low-latency, ad-hoc analysis of data
- Can process data from multiple data sources including the HDFS and Amazon S3
NoSQL Applications
Apache HBase
- Non-relational, distributed database modeled after Google’s BigTable
- Runs on top of HDFS to provide BigTable-like capabilities for Hadoop
- Store large amounts of sparse data using column-based compression and storage
- Use S3 as a data store for HBase, enabling you to lower costs and reduce operational complexity
Interactive Analytics Applications
Hue
- User Interface for Hadoop that allows you to create and run Hive queries, manage files in HDFS, create and run Pig scripts, and manage tables
- Also integrates with S3, so you can query directly against S3 and easily transfer files between HDFS and Amazon S3
EMR Notebooks
- Notebooks pre-configured for Spark that are based on Jupyter notebooks
- Interactively run Spark jobs on EMR clusters written in PySpark, Spark SQL, Spark R or Scala
Optimizing EMR
Based on your workload you have several options for optimizing your EMR cluster. Design options:
- Instance type
- Instance configuration
- HDFS capacity
- Dynamic sizing
- Instance fleets or uniform instance groups
- Run multiple steps in parallel
EMR Instance Types
Ways to add EC2 instances to your cluster.
Instance Groups:
- Manually add instances of the same type to existing core and task instance groups
- Manually add a task instance group, can use different instance type
- Automatic scaling for an instance group based on the value of a CloudWatch metric specified by you
Instance Fleets:
- Add a single task instance fleet
- Change the target capacity for on-demand and Spot Instances for existing core and task instance fleets.
Best Practices:
- Plan your instance capacity:
- Run a test cluster using a representative sample data set and monitor the node utilization
- Calculate instance capacity and compare that value against the size of your data
- Master node does not require high computational capacity
- Most EMR clusters can run on m5.xlarge or m4.xlarge
- Data processing load performance depends on the capacity of your core nodes and data size as input, during processing, and as output
EMR Intance Configuration
Long-running clusters and data warehouses
- Persistent EMR cluster (e.g. Data Warehouse)
- Master and core instance group as on-demand instances
- Task instance group as spot instances
Cost-driven workloads
- Low cost, partial work loss OK
- Transient clusters automatically termiante after all steps are complete. This will lower your operational costs by not leaving the EMR nodes running when they are not in use.
- Run all groups, master core, core, and task instance groups as spot instances
Data-critical workloads
- Low cost, partial work loss not OK
- Master and core instance groups as on-demand, task instance groups as spot
Test environment
- All instances groups on spot
Remarks:
- EMR long-running clusters must be manually terminated when they are no longer needed. Therefore this option will not give you the same cost-effectivness as a Transient Cluster
- EMR Core Nodes run HDFS. Therefore, if a Core Node is terminated through the spot instance process, you will lose your data stored in HDFS
- EMR Task Nodes do not store data in HDFS. If you ose your Task Node through the spot instance process, you will not lose data stored on HDFS.
- When you launch an EMR cluster via the AWS CLI, the default is to have auto-terminate disabled. This will, in effect, create a long-running cluster.
EMR HDFS Capacity
To calculate the storage allocation for you cluster consider the following
- Number of EC2 instances used for core nodes
- Capacity of the EC2 instance store for the instance type used
- Number and size of EBS volumes attached to core nodes
- Replication factor: how each data block is stored in HDFS for RAID-like redundancy
- 3 for a cluster of 10 or more core nodes, 2 for a cluster of 4-9 core nodes, and 1 for a cluster of three or fewer nodes
- HDFS capacity of you cluster
- For each core node, add instance store volume capacity to EBS storage capacity
- Multiply by the number of core nodes, then divide the total by the replication factor
EMR Dynamic Sizing
Dynamically scales nodes in your cluster based on demand
- On scale down of task nodes on a running cluster expect a short delay for any running Hadoop to decommission
- On scale down of core nodes EMR waits for HDFS to decommission to protect your data
- Changing configuration improperly on a cluster with high load can seriously degrade cluster performance
EMR Instance Fleets vs Uniform Instance Groups
- Choice applies to all nodes for the lifetime of the cluster
- Instance fleets and instance groups cannot coexist in a cluster
Instance fleets:
- Each node type has a single instance fleet; task instance fleet is optional
- Up to 5 instance types (if using allocation strategy, up to 15 instances types on task instance fleets), which can be provisioned as on-demand and Spot Instances
- Mix of specified instance types to reach target capcities: On-Demand and Spot Instances
- Core and task instance fleets: assign a target capcity for On-Demand Instances, and another for Spot Instances
Uniform Instance Groups
- Simplified, up to 50 instance groups: 1 master instance group containing 1 EC2 instance, core instance group containing one or more EC2 instances, up to 48 optional task instance groups
- Scale each instance group by adding and removing EC2 instances manually, or set up automatic scaling
Run Multiple Steps in Parallel
- Allows for parallel processing and greater speed
- Considerations
- Use EMR automatic scaling to scale up/down based on the YARN resouroces to prevent resource contention
- Running multiple steps in parallel requires more memory and CPU utilzation from the master node than running one step at a time
- Use YARN scheduling features such as FairScheduler or CapacityScheduler to run multiple steps in parallel
- If you run out of resources because the cluster is running to many concurrent steps, manually cancel any running stepts to free up resources
Respond to State Changes on EMR Cluster
Trigger create, terminate, scale cluster, run Spark, Hive, or Pig workloads based on Cluster state changes
- EMR CloudWatch events support notify you of state changes in your cluster
- Respond to state changes programmatically
- EMR CloudWatch events
- Cluster State Change
- Instance Group and Instance Fleet State Change
- Step State Change
- Create filters and rules to match events and route them to SNS topics, Lambda functions, SQS queues, Kinesis Streams
Use CloudWatch Metrics to Manage EMR Cluster
EMR metrics updated every 5 minutes, collected and pushed to CloudWatch
- Non-configurable metric timming
- Metrics archived for two weeks then discarded
EMR metrics uses
- Track progress of cluster:
RunningMapTasks,RemainingMapTasks,RunningReducedTasks, andRemainingReduceTasks - Detect idle clusters:
IsIdlemetric tasks if a cluster is live, but not currently running tasks. Set an alarm to fire when the cluster has been idle for a given period of time - Detect when a node runs out of storage:
HDFSUtilizationmetric gives the percentage of disk space currently used. If it rises above an acceptable level for your application, such as 80% of capacity used, you take an action to resize your cluster and add more core nodes
View and Monitor EMR Cluster
EMR has several tools for retrieving information about your cluster
- Console, CLI, and API
- Hadoop web interfaces and logs on Master node, e.g. Hue
- Use monitoring services like CloudWatch and Ganglia to track the performance of your cluster
- Application history available through persistent application UIs for Spark History Server, persistent YARN timeline Server, and Tez user interfaces
Leverage EMR API Calls in CloudTrail
CloudTrail holds a record of actions taken by users, roles, or an AWS servie in EMR
- Captures all API calls for EMR as events
- Enable continous delivery of CloudTrail events to an S3 bucket
- Determine the EMR request, the IP address from which the request was made, who made the request, when it was made, and additional details
Orchestrate Spark and EMR workloads using Step Functions
- Use Apache Oozie or Apache Airflow scheduler tools for EMR Spark applications
- Use Step Functions and interact with Spark applications on EMR using Apache Livy
- Directly connect Step Functions to EMR
- Create data processing and analysis workflows with minimal code and optimize cluster utilization