IAM Authentication
To set permissions for an identity in IAM, choose an AWS managed policy, a customer managed policy, or an inline policy.
AWS managed policy
- Standalone policy that is created and administered by AWS
- Provide permissions for many common use cases: full, power-user, and partial access
Customer managed policy
- Standalone policies that you administer in your AWS account
Inline policy
- strict one-to-one relationship of policy to identity
- Policy embedded in an IAM identity (a user, group or role)
Security Use Cases
IAM best practices of how to apply IAM and other access controls
IAM User
- Use AWS CLI to create resources in AWS account
IAM Role
- Create Glue crawlers and ETL jobs that access S3 buckets
- Single sign on into corporate network and applications
Cognito
- Web application that needs to access DynamoDB through a REST endpoint
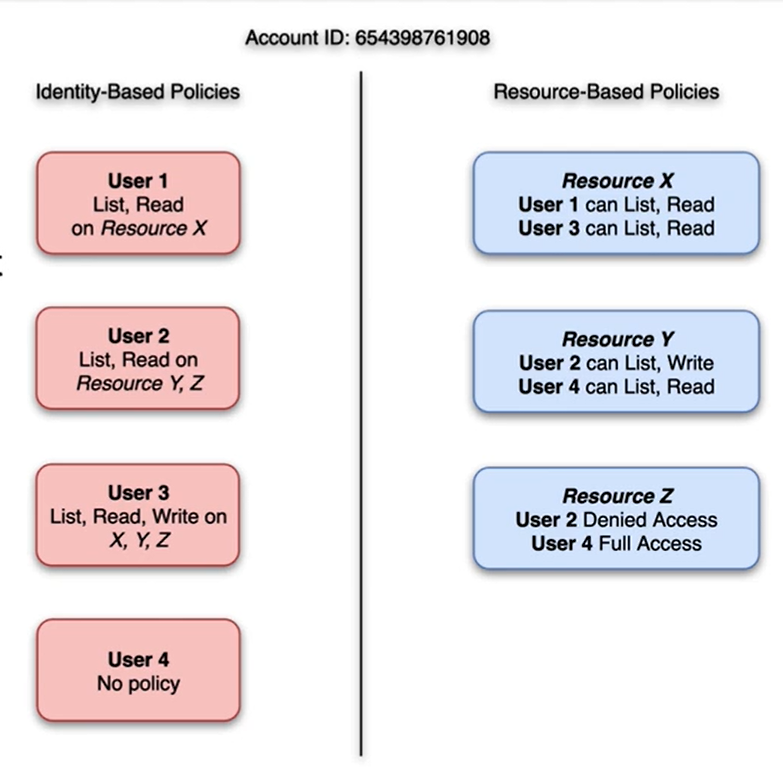
IAM Authorization
- Use IAM identity- and resource-based permissions to authorize access to analytics resources
- Policy is an object in AWS you associate with an identity or resource to define the identity or resource permissions
- To use a permissions policy to restrict access to a resource you choose a policy type
- Identity-based policy
- Attached to an IAM user, group or role
- Specifiy what an identity can do (its permissions)
- Example: attach a policy to a user that allows that user to perform the EC2 RunInstances action
- Resource-based policy
- Attached to a resource
- Specify which users have access to the resource and what actions they can perform on it
- Example: attach resource-based policies to S3 buckets, SQS queues, and Key Management Service encryption keys
- Identity-based policy
Network Security - Using VPCs to Isolate Your Resources
Need to secure the pyhsical boundary of your analytics services using network isolation
EMR - Managed Security Groups
- Every EMR cluster has managed security groups associated with it, either default or custom
- EMR automatically adds rules to managed security groups used by the cluster to communicate between cluster instances and AWS services
- Rules that EMR creates in managed security groups allow the cluster to communicate among internal components
- To allow users and applications to access a cluster from outside the cluster, edit rules in managed security groups
- Editing rules in managed security groups may have unintended consequences; may inadvertently block the traffic required for clusters to function properly
- Specify security groups only on cluster create, can NOT add to a cluster or cluster instances while a cluster is running
- Can edit, add, and remove rules from existing security groups, the rules take effect as soon as you save them
EMR - Additional Security Groups
- Additional security groups are optional
- Specify in addition to managed security groups to tailor access to cluster instances
- Contain only rules that you define, EMR does not modify them
- To allow users and applications to access a cluster from outside the cluster, create additional security groups with additional rules.
EMR - VPC Options - Security Groups
- At EMR cluster launch, must specify one EMR-managed security group for the master instance, one EMR-managed security group for the core/task instances, and optionally, one EMR-managed security group for the EMR resources used to manage clusters in private subnets
- The core/task instances share the same security group

EMR - VPC Options - S3 Endpoints & NAT Gateway
S3 Endpoints
- All instances in a cluster connect to S3 through either a VPC endpoint or internet gateway
- Create a private endpoint for S3 in your subnet to give your EMR cluster direct access to data in Amazon S3
NAT Gateway
- Other AWS services which do not currently support VPC endpoints use only an internet gateway
Encryption and Tokenization
Protect data against data exfiltration (unauthorized copying and/or transferring data) and unauthorized access
Different ways to protect data
- Use a hardware security module (HSM) to manage the top-level encryption keys
- Encryption at rest
- Encryption in transit
- Alternative to encryption to secure highly sensitive subsets of data for compliance puroposes
- Secrets management
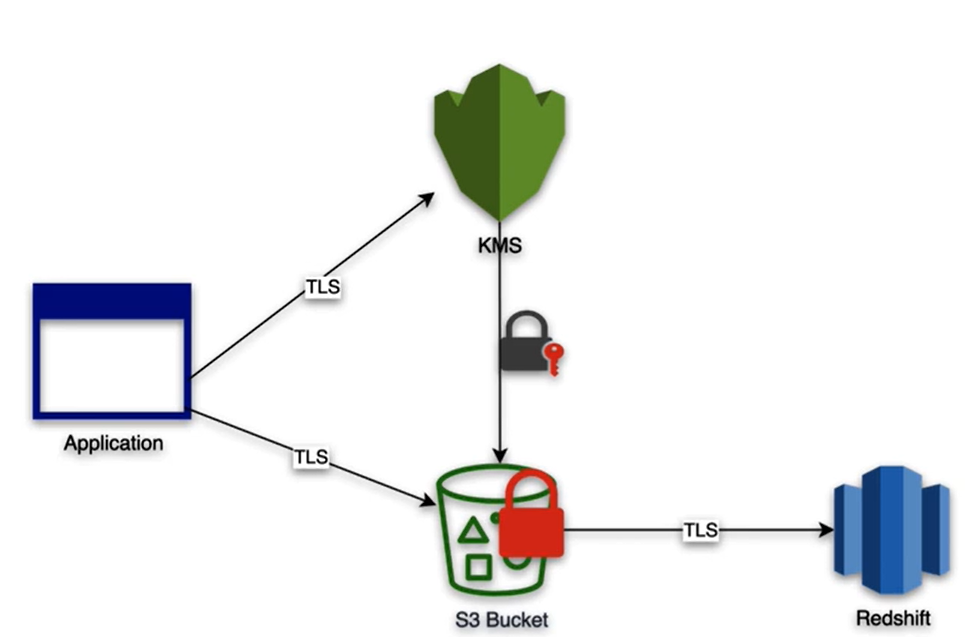
HSM
Use HSM
- if you require your keys stored in dedicated, third-party validated hardware security modules under your exclusive control
- if you need to comply to FIPS 140-2
- If you need high-performance in VPC cryptographic acceleration (bulk crypto)
- if you need a multi-tenant, managed service that allows you to use and manage encryption keys
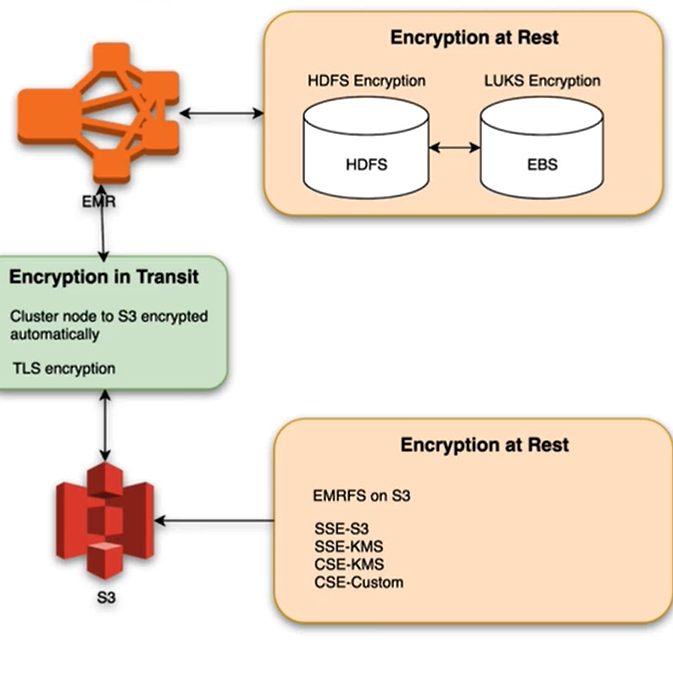
Encryption at Rest and In Transit - EMR
- Prevent unauthorized users from reading data on a cluster and associated data storage systems
- Encryption at rest: data saved to persistent media
- Ecryption in transit: data that may be intercepted as it travels the network
- Use EMR security configurations to configure data encryption settings for clusters
- Enable security for data in-transit and dat at-rest in EBS volumes and EMRFS on S3
- EMR release version 4.1.0 and later, you can configure transparent encryption in HDFS, which is not configured using security configurations
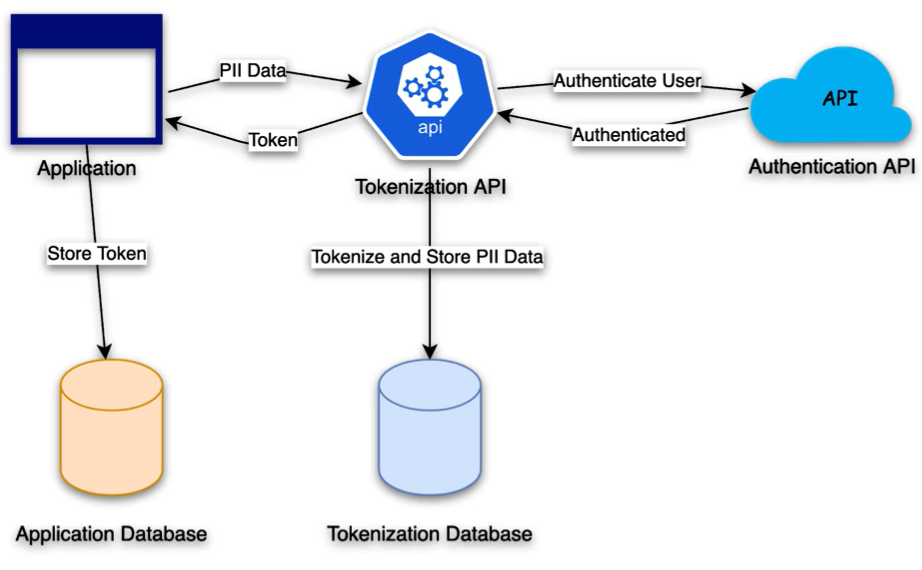
Tokenization
- Protect certain elements in the data contains high sensitivity or a specific regulatory compliance requirement, such as PCI
- Separates sensitie data into its own dedicated, secured data store
- Use tokens to represent sensitive data instead of end-to-end encryption
- Reduce risk with temporary, one-time-use tokens
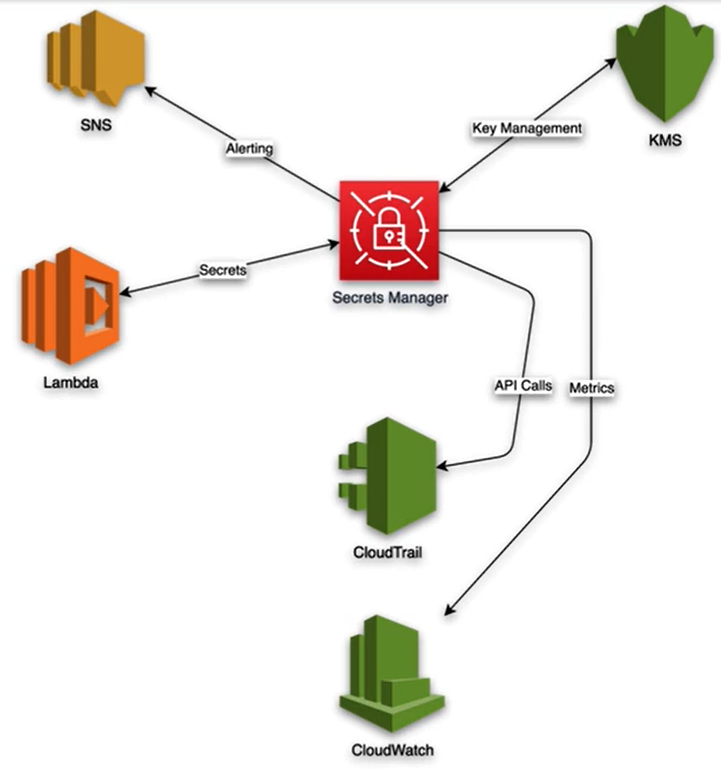
Secrets Management
Secrets Manager
- use secrets in application code to connect to databases, APIs, and other resources
- Provides rotation, audit, and access control
Systems Manager Parameter Store
- Centralized store to manage configuration data
- Plain-text data such as database strings or secrets such as passwords
- Does not rotate parameter stores automatically
Compliance and Governance
- Identify required compliance frameworks (HIPAA, PCI, etc.)
- Understand contractual and agreement obligations
- Monitor policies, standards, and security controls to respond to events and changes in risk
- Services to create compliant analytics solution
- AWS Artifcat: provides on-demand access to AWS compliance and security related information
- CloudTrail and CloudWatch: enable governance, compliance, operational auditing, and risk auditing of AWS account
- AWS Config: ensure AWS resources conform to your organization’s security guidelines and best practices
AWS Artificat
- Self-service document retrieval portal
- Manage AWS agreements: NDAs, Business Associate Addendum (BAA)
- Produce security controls documentation: provide AWS artifact compliance documents to regulators and auditors
- Download AWS security and compliance documents, such as AWS ISO certifications, PCI, and SOC reports
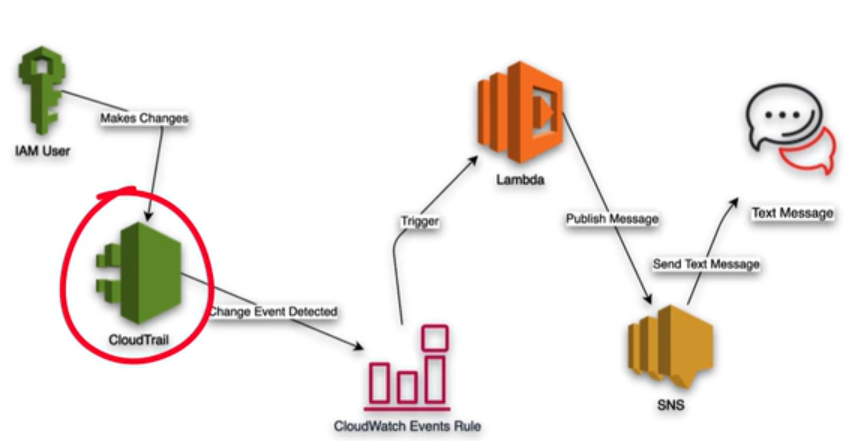
CloudTrail and CloudWatch
- CloudTrail tracks actions in your AWS account by recording API activity
- CloudWatch monitors how resources perform, collecting application metrics and log information
- Simplify security analysis, resource change tracking, and troubleshooting by combining event history monitoring via CloudTrail and resource history via CloudWatch
- Use CloudTrail to audit and review API calls and detect security anomalies
- Use CloudWatch to create alert rules that trigger SNS notifications or Lambda functions that run in response to a security or risk event
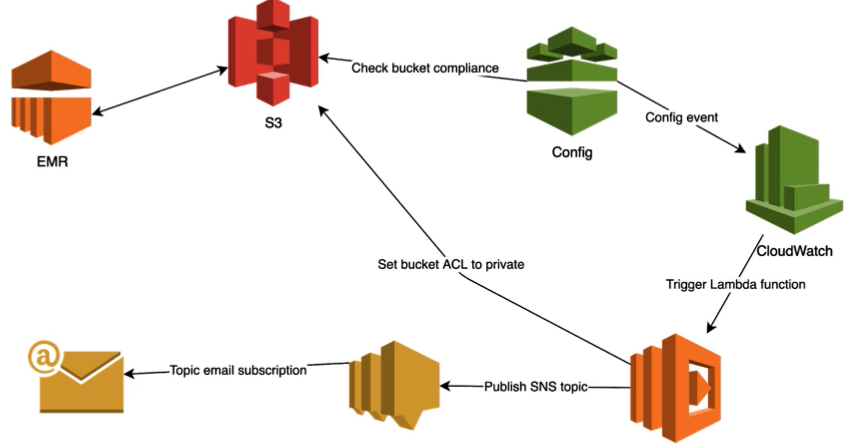
AWS Config
- AWS resource inventory, configuration history, and configuration change notifications that enable security and governance
- Discover existing AWS resources
- Export complete inventory of account AWS resources with all configuration details
- Determine how a resource was configured at any point in time
- Config Rules: represent desired configurations for a resource and is evaluated against configuration changes on the relevant resources, as recorded by AWS config
- Assess overall compliance and risk status from a configuration perspective, view compliance trends over time and pinpoint which configuration change caused a resource to drift out of compliance with a rule
Other Amazon Services for Security
Amazon Inspector Amazon Inspector is an automated security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS.
Amazon GuardDuty Amazon GuardDuty offers conitnuous monitoring of your AWS accounts and workloads to protect against malicious or unauthorized activites.
Macie Macie is used for data security and data privacy service with pattern matching to discover and protect sensitive data in AWS.